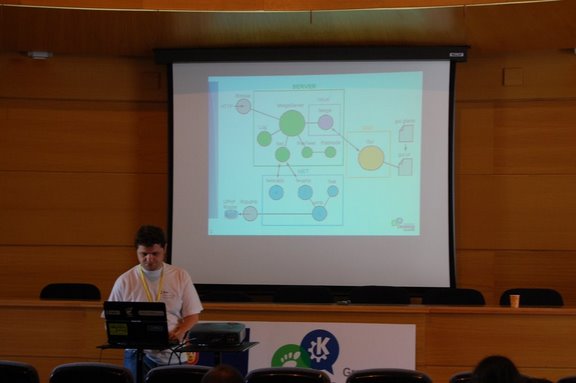
These months I’ve been collaborating in Libertexto development. Libertexto, a project coordinated by Rafael Ibáñez, will be a Firefox extension whose goal is to allow the user to do some text comprehension tasks (highlight, add annotations and create bookmarks) and concept mapping tasks (manage a tree of “lexias” or units with semantic content) on HTML and PDF documents.
Multiplatform
So far, I’ve mainly been involved in the task of integrating Evince into Firefox. The goal was not only to provide support for PDF document viewing, but also to adapt Evince to manage the communication with the Firefox extension and to provide the required functionalities and GUI interaction. The fact that Libertexto has to work both in Linux (Ubuntu Jaunty) and Windows made the task more challenging and had an important influence in the design decissions.
The plugin
The main idea was to write a plugin registered to visualize documents having the “application/pdf” mime type, using Evince for that, and interact with the XUL/Javascript code to coordinate everything. The npsimple (check my npsimple backup link) example was very valuable to learn how to code a multiplatform basic plugin implementing the Netscape Plugin API (NPAPI). These first testings (with the help of Dependency walker) showed me that the plugin code would only load if compiled with the same compiler used to build Firefox. That means forgetting Cygwin, MinGW32 and other Windows platform free stuff and compile using Visual C++, getting the headers from the Mozilla SDK.
Communications: first try
Once I had a plugin that did nothing, I looked for ways to communicate it with Firefox. I tried some XPCOM examples and debug tools without much luck, so I finally decide to use alternative ways of communication when I needed to.
Compiler restrictions
At this point I focused in compiling Evince for Windows. I chose Evince 2.28.0 because it had been already compiled for Windows by Hib Eris. I found him in the #evince IRC channel and he pointed me to the Ubuntu PPA he had used to cross compile for Windows using MinGW32. He also confirmed to me that mixing MinGW32 compiled apps with MSVC compiled apps is a problem because MinGW32 compilations are dependant on msvcrt.dll, while recent MSVC compilations depend on msvcrt80.dll or msvcrt90.dll. That explains why I couldn’t compile the plugin with the MinGW32 toolchain from Windows. Forget also about converting Evince itself into a plugin (implementing NPAPI), because it won’t load. There’s currently no easy solution, but to compile everything with MSVC (not tried before) or keep applications split.
Embedding the window
After having compiled Evince and all its dependencies for both operating systems I modified the plugin to start Evince each time a new document was loaded. Next step was to find a way to embed Evince in Firefox, because having it as an independent window was not an option. The plugin was given a window ID (XID in X11, HWND in Windows), so I modified Evince to receive it as an extra parameter and use gtk_window_reparent() to “hijack” the window that Firefox provided. Of course, using Mozplugger is much easier, but it’s not supported in Windows, so I had to do it by hand. After some tweaking and having to disable DBUS support to get exactly one process per document (in Linux), it worked in both systems. In Windows I ended up with refresh and focus problems, but I didn’t go further.
Communications: second try
At this point, the key was to have a reliable communication system between Evince and the plugin. DBUS would have been good for Linux, but would bring too much problems in Windows (everything should be installed or work from the Firefox extension bundle and I’d need a way to use DBUS from javascript). Standard IPC methods (eg: shared memory) would be a problem too, because I hadn’t managed to successfully develop XPCOM components that could access low level C functions to use that IPC methods. However, there’s one thing that always work: plain old HTTP requests. They are supported in the Firefox side using XMLHttpRequest and in the Evince side using libsoup-2.4. I had experience using libsoup in Meiga, so it wasn’t difficult for me to set up a bidirectional realtime communication middleware using the AJAX paradigm.
The initial port handshake is a bit tricky, though. Remember that there’s no way for the Firefox extension, the plugin and Evince to talk to each other before this handshake. The process is as follows:
- The user opens a URL containing a PDF, so the PDF plugin is invoked. If the plugin is in Linux and detects that libertexto hasn’t been installed in
/usr/local/libertexto-0.0.5 yet, it triggers the install script and waits until the process is completed. Then continues.
- Using dll/so API calls on the first load, the plugin gets the path where
nplibertexto.dll/.so is installed (eg: /home/user/.mozilla/firefox/ky712h81.default/extensions/libertexto-0.0.5@libresoft.es/platform/Linux_x86-gcc3). From that path it gets the extension path (...libertexto-0.0.5@libresoft.es) and builds the xid directory path (...libertexto-0.0.5@libresoft.es/xid)
- The plugin gets the URL and the downloaded file name through NPAPI. It then launches Evince (fixed location in Linux, variable location under the extension dir in Windows) with the following parameters:
evince --xid 0x6800001 --libertexto-path /home/user/.mozilla/firefox/ky712h81.default/extensions/libertexto-0.0.5@libresoft.es/xid /home/user/local_links.pdf.
- Evince opens the file, hijacks the window with handler 0x6800001 and starts a web server on a random port of 127.0.0.1 which will wait for incoming connections. Then the port number is written to a file named
0x6800001 in the xid directory.
- The plugin has been waiting up to 5 seconds and monitoring the xid directory for new files. When it finds a new one, reads it and inserts the (xid, process id, MD5 sum of the URL, port) into a
children array for further use. Each time the children array changes, the file libertexto-0.0.5@libresoft.es/libertexto-docs is regenerated. That file has the URL MD5 sum and port, one line per document.
- The file is available as
resource://libertexto-docs/ to the Firefox extension and it’s monitored each 5 seconds using XMLHttpRequest (it can also read local files). That way, the extension keeps a table of open documents and their ports.
- Each time the extension detects a new entry in the table, it connects to the port using XMLHttpRequest on a special “receive” URL (eg:
http://127.0.0.1:53162/receive) and reads and attends any pending messages that Evince would like to communicate. If there are no more messages, just keeps waiting for one to come. When one comes, the network dispatcher in the Libertexto extension attends it, closes the connection and restarts it to wait again. Evince code just enqueues outgoing messages and writes them when the extension (re)opens the connection.
- If it’s the extension who wants to send a message to Evince, a request is made to a “send” url (eg:
http://127.0.0.1:53162/send?action=test¶m1=value1¶m2=value2). There’s also another network dispatcher in Evince that processes incoming messages and calls the corresponding function of EvApplication.
- When the document is closed, the plugin code is informed by NPAPI and just ensures that Evince is killed, the
0x6800001 xid file is removed and libertexto-docs is rebuilt.
Packaging
It was time to polish a little bit the building and packaging environment. Different binary sets for different platforms can be provided using the platform directory in the Firefox extension package. In Windows, there’s no problem in relocating a GNOME app where you want, as there’s specific code to locate the data and config dirs, but in Linux it has to be installed in a fixed location, so I prepared a very basic installation script for that platform to be executed by the plugin the first time that the user opens a document.
Functionalities
With the infrastructure ready, I started to hack on Evince and implement the required functionalities (and the related middleware messages in both sides):
- Get the text directly selected by the user
- Scroll to a specified position of a specified page in a document
- Highlight some (preselected) text with the specified color
- Set an “start of selection” internal mark
- Set an “end of selection” internal mark and then select the text between the start and the end of selection
- Show the “create new item” option in the context menu and pass that command to the Firefox extension
- Overimpress an annotation with some arbitrary text
- Overimpress some icons that would trigger some commands on the current items
For some of them, specially those related to text highlighting and annotations, the advice from Carlos García Campos was very helpful. Shell, view, document and backend layers, the pixbuf cache, the jobs system… Evince is a big project and I needed some time to get used and understand it, but it has a lot of things to learn. I enjoyed very much this development stage. 🙂
When all the PDF side functionalities were completed, I removed all the unneeded GUI options from Evince and adapted the Libertexto extension panel to produce and handle the required middleware messages needed to manage the user interaction.
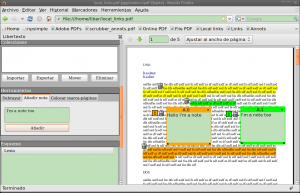
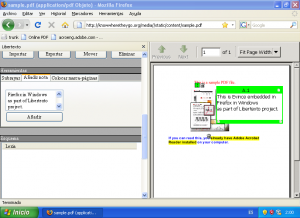
The result
Although the project still lacks part of the control and HTML modules functionalities, I got Evince integration working in this nice prototype.
You can download it as: libertexto.xpi (UPDATE 3/3/2011: you might prefer to download the final Libertexto 1.0 version). Please note that this file will probably evolve, being overwritten with newer versions.
Until the whole project gets released, a shapshot of the Evince branch code is published in Gitorious for you to have a look.


 This weekend I’ve taken advantage of our hackfest sessions at Igalia winter summit and have prepared a new “Halloween” version of Meiga.
This weekend I’ve taken advantage of our hackfest sessions at Igalia winter summit and have prepared a new “Halloween” version of Meiga.